What is a Traceability System?
Ensuring Visibility, Safety, and Accountability Across the Supply Chain
📌 Introduction
In today’s global economy, traceability isn’t just a feature—it’s a necessity. Whether it’s a food item, pharmaceutical product, industrial component, or consumer good, businesses and consumers alike want to know: Where did it come from? Where is it going? And is it safe?
A traceability system answers all these questions by tracking the origin, movement, and history of products across the supply chain—from raw material to end-user.
1: “End-to-End Product Journey Map”
(Show a visual flow of a product going from supplier → manufacturer → warehouse → retailer → customer)
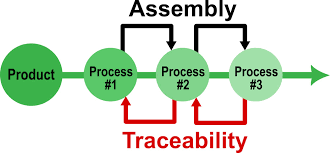
🧩 What is a Traceability System?
A traceability system is a digital or physical process used to identify, track, and trace the path of products or components throughout their lifecycle.
It allows companies to:
- Track (follow the path forward) a product through each stage
- Trace (look back) to where the product or its materials came from
🔄 Two Types of Traceability
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Forward Traceability | Tracks a product from creation to the end-user | From raw materials to store shelves |
| Backward Traceability | Traces back from the finished product to the original source | Identifying which batch of raw materials was used in a recalled product |
“Forward and Backward Traceability Diagram”
(Use arrows and product icons to show forward vs backward movement of data/information)

🛠️ How Does a Traceability System Work?
- Identification: Each product or batch is assigned a unique ID (barcode, QR code, RFID, or serial number).
- Data Collection: At every stage—production, packaging, storage, shipping—data is recorded.
- Storage: Information is stored in a centralized database or cloud platform.
- Tracking/Tracing: Businesses use software to monitor movement, generate reports, or initiate recalls.
- Analysis & Compliance: Data helps with audit trails, regulatory reporting, and quality control.
3: “Traceability Workflow Chart”
(Flowchart showing stages like: Supplier → Manufacturing → Quality Control → Warehouse → Delivery)

📦 Technologies Used in Traceability Systems
| Technology | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Barcodes (1D/2D) | Item identification and scanning |
| RFID Tags | Wireless tracking in warehouses and logistics |
| QR Codes | Consumer-facing traceability (scans via smartphones) |
| IoT Devices | Real-time tracking of environmental conditions (temp, humidity) |
| Blockchain | Secure, tamper-proof traceability records |
| ERP Systems | Centralized management and reporting |
4: “Sample Barcode/QR Code on Product Label”
(Show a product label with barcode/QR code linked to a traceability system)

🧠 Why is Traceability Important?
✅ 1. Product Safety & Recalls
- Instantly identify and isolate affected products in case of contamination or defect.
✅ 2. Regulatory Compliance
- Comply with laws like FSSAI (India), FDA (USA), GS1 standards, or EU MDR for medical devices.
✅ 3. Inventory Optimization
- Track inventory in real time to reduce overstocking or stockouts.
✅ 4. Quality Control
- Pinpoint where defects occur and improve upstream processes.
✅ 5. Consumer Trust
- Let end-users verify the origin, authenticity, and ethical sourcing of products.
🖼️ Image Suggestion 5: “Mobile App Showing Product Origin Scan”
(Simulated smartphone screen scanning QR on a product to show its journey or origin)
🏭 Industries That Rely on Traceability
| Industry | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Track farm-to-fork, recall contaminated items |
| Pharmaceuticals | Prevent counterfeits, comply with DSCSA |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Track components, ensure safety compliance |
| Retail | Inventory tracking, returns management |
| Healthcare | Medical device and patient care traceability |
| Textile & Fashion | Ethical sourcing, fast-moving goods tracking |
🧱 Benefits of a Traceability System
- 🔍 Transparency across supply chains
- 🕒 Faster recalls and reduced risk
- 💰 Cost savings from better inventory control
- 📈 Improved brand value through trust and accountability
- 📑 Regulatory readiness with real-time reports and audit trails
⚠️ Challenges in Implementing Traceability
While powerful, traceability systems come with implementation challenges:
- Integration with legacy systems
- Upfront hardware/software costs
- Employee training
- Labeling and data standardization
- Managing large volumes of data
🚀 Future of Traceability: What’s Next?
- AI & Predictive Analytics – To detect supply chain disruptions.
- Blockchain-Based Systems – For immutable records and decentralized transparency.
- Digital Twins – Virtual replicas of physical supply chains.
- Mobile Traceability – Consumers scanning to see origin and sustainability data.
- Sustainability Metrics – Carbon footprint, water usage, and ethical labor tracking.
📝 Conclusion
Traceability systems are no longer optional—they are essential for operational efficiency, compliance, and consumer confidence. Whether you’re in food manufacturing, pharma, logistics, or retail, traceability ensures you’re equipped to handle recalls, maintain quality, and meet global standards.
By combining barcoding, digital platforms, and real-time data, businesses can transform their supply chain into a transparent, secure, and future-ready ecosystem.
SavTech, a leading provider of smart automation solutions, integrates advanced barcode traceability systems within its suite of enterprise software. Our solutions are designed to streamline warehouse, production, and logistics operations for enhanced visibility, accountability, and compliance. With SavTech’s expertise, businesses gain not only a powerful tracking system but also a strategic advantage in operational excellence and customer satisfaction.


2 responses to “Barcode Traceability System”
[…] document explores the complete workflow and importance of product labeling and packaging, followed by how traceability is achieved through barcode and QR code scanning systems, […]
[…] Without barcodes, traceability is impossible. Barcodes identify products, assets, and shipments in a supply chain. Here’s how barcodes contribute to traceability: […]